New England home heating and electricity prices are on the rise with no end in sight. Consumers paid record high energy bills last winter, even though the winter was not unusually cold. Shortages of natural gas and green energy policies will drive New England prices higher and raise the chance of electricity blackouts.
Residential energy bills in New England this year were the highest in history. The combination of electricity and natural gas heating bills exceeded $1,000 per month for an average-sized house in Massachusetts, even though winter temperatures in New England were warmer than average.
Eighty percent of homes in New England, which includes Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont, heat with fuels from oil and gas. The hydrocarbon fuel share of home heating is natural gas (39%), fuel oil and kerosene (33%), and propane or liquid petroleum gas (8%). Homes also use electricity (16%) and other sources (4%) for heat.
Natural gas is also the leading fuel for generation of electricity. New England power comes from natural gas (43%), nuclear (21%), imports (17%), hydroelectric (6%), renewables (12%), and other generators (1%). But New England residents now pay higher prices for natural gas than the rest of the nation and gas prices are rapidly rising.
For the last decade, the State of New York blocked the construction of natural gas pipelines as part of efforts to decarbonize. For example, the Constitution Pipeline project was cancelled in 2019 after an eight-year battle. Plans called for the pipeline to connect natural gas fields in Pennsylvania to the gas network in Schoharie County, just west of Albany, New York. Because New York is blocking pipeline delivery, New England is forced to import liquified natural gas (LNG) for home and electrical power generation.
New Englanders now pay more than twice the price for natural gas than most other US residents pay, and that gap is growing. During peak periods, the Citigate Massachusetts price for gas now rises to more than $10 per million BTU, much higher than the US average Henry Hub typical price of $3-4 per million BTU. Because pipeline capacity is low, New England must import up to 30 percent of its gas by LNG tanker and pay high world market prices. During the recent global energy crisis, Massachusetts was paying $40-$50 per million BTU for imported LNG.

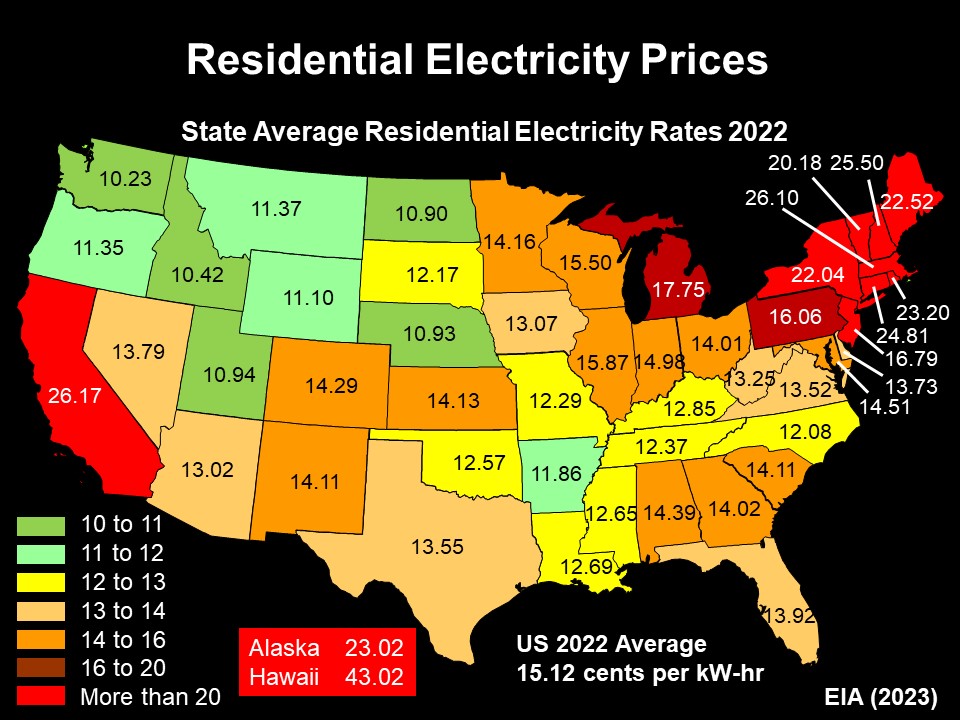
New England electricity prices are also among the highest in the nation. In 2022, power prices for all six of the New England states were over 20 cents per kilowatt-hour, and all in the top ten for state electricity prices. Massachusetts residential customers paid 26.1 cents per kW-hr, surpassed only by prices in Hawaii and California.
The risk of electricity blackouts in New England is rising. The Interstate Natural Gas Association of America sent a letter to President Joe Biden last November, warning that the region “does not have sufficient pipeline infrastructure” and is “at risk of an energy shortfall.” ISO New England, the non-profit organization responsible for reliable electricity in New England, wrote a similar warning letter to Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm last summer, stating, “during the coldest days of the year, New England does not have sufficient infrastructure to meet the region’s demand for natural gas for both home heating and power generation.” But government leaders and environmental groups oppose further expansion of natural gas infrastructure.
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission and ISO New England have proposed a shift in LNG pricing to allow purchase and stockpiling of natural gas in New England to prevent a winter fuel shortage. This price shift would raise consumer prices and is opposed by New England states and environmental groups. The pipeline capacity shortage and inadequate gas stockpiles have set the stage for electricity blackouts in the region during the next severe winter.
New England state governments remain committed to construction of offshore wind turbines and providing incentives for electric heat pumps as part of a misguided effort to fight climate change. But these programs, if completed, will not make the grid more reliable and will further boost energy costs.
New England homeowners, better get yourself a backup electric generator and prepare for further rises in home heating and electricity prices.
Steve Goreham is a speaker on energy, the environment, and public policy and an author of three books on energy, sustainable development, and climate change.





